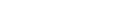Ad
Ad
Mastering Tractor Power: Complete Guide to Transmission System, Parts, Types & Functions for Smarter Farming
When buying a tractor, most people look at horsepower, mileage, and brand reputation. However, one of the most important, yet often overlooked, aspects of a tractor is its transmission system. It acts as the tractor’s backbone, delivering power from the engine to the wheels and controlling how efficiently it performs on the field.
This detailed guide will help you understand what a tractor transmission system is, its main components, the different types of transmissions used in tractors, and how they all work together to power your tractor efficiently.
Also Read: Comprehensive Guide to Tractor Transmission System: Types, Functions, and Future Innovations
What is Transmission in Tractors?
In simple terms, transmission in a tractor means the system that transfers power from the engine to the wheels. It is usually located behind the engine and is made up of several mechanical parts like gears, shafts, and clutches.
The transmission system allows farmers to change the tractor’s speed, torque, and direction according to their needs. It ensures that the tractor can handle various tasks, from slow, heavy work like ploughing to faster tasks like transport.
Main Functions of a Tractor Transmission System:
To change the speed of the tractor as per the type of work.
To provide more torque at low speeds for heavy field operations.
To control forward and reverse movements.
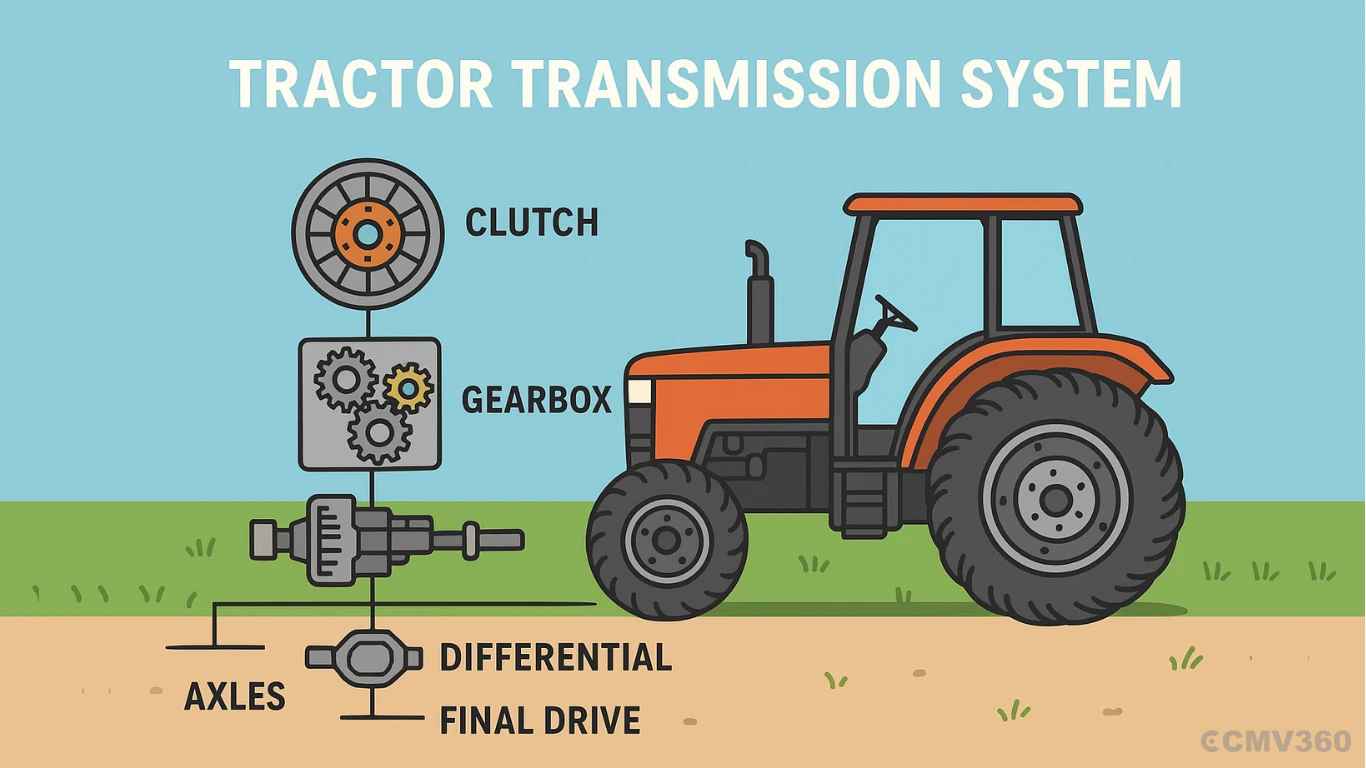
A tractor transmission system is not a single part but a network of multiple components, including the clutch, gearbox, differential, final drive, and axles. Together, these elements form the core of the tractor’s performance system.
Also Read: More Work with Less Diesel: 7 Easy Tips to Increase Tractor Mileage and Save Farming Costs
Main Components of a Tractor Transmission System
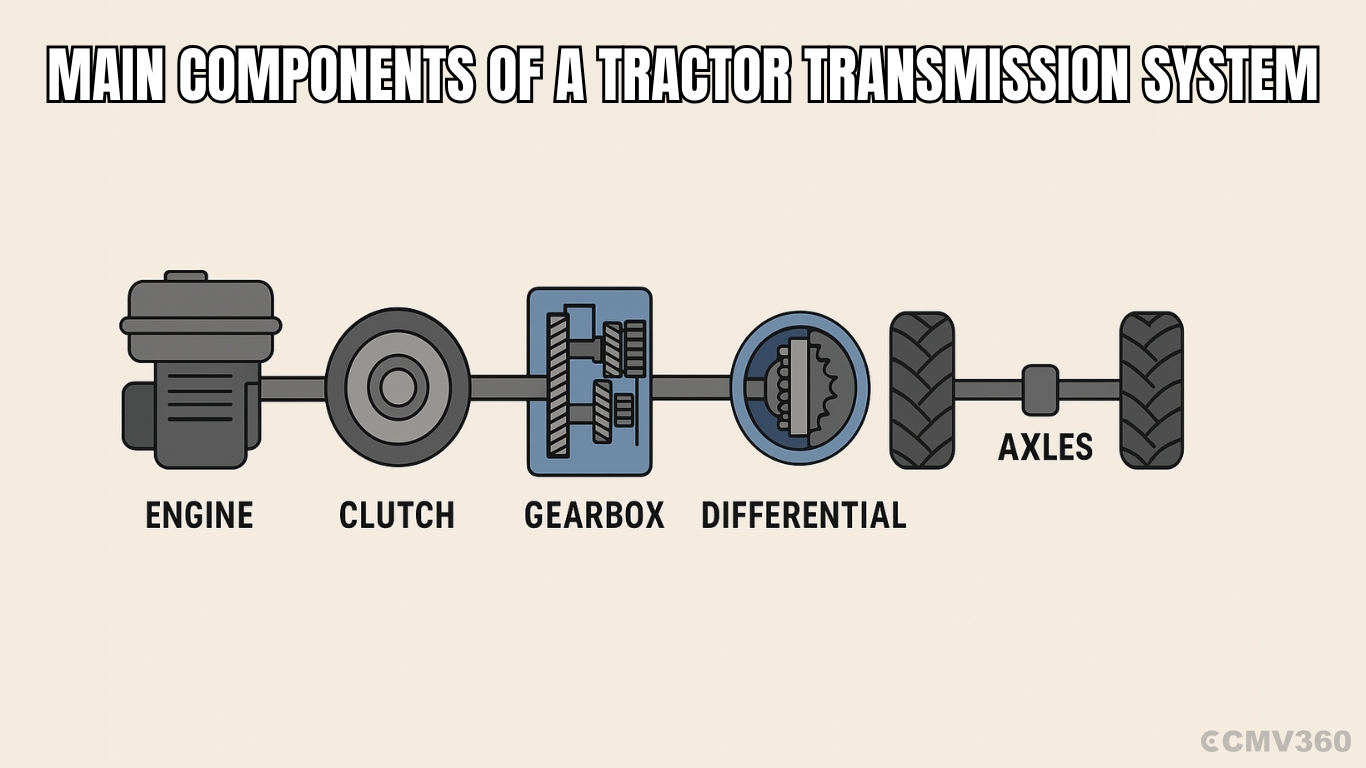
Let’s explore the key components that make up the tractor transmission system and understand how each one functions.
1. Clutch: The Power Connector
The clutch connects and disconnects the engine from the transmission system. It helps the driver change gears, stop the tractor, or operate implements without stopping the engine.
When you press the clutch pedal, it disconnects the engine’s power temporarily, allowing you to shift gears smoothly. Once you release it, power flows again to the wheels and PTO (Power Take-Off).
There are different types of clutches based on how they function and how they are lubricated.
Types of Tractor Clutches:
A. Based on Control Mechanism:
Single Clutch: It has one clutch plate and one pedal controlling both the wheels and the PTO shaft. When you change gears or stop the tractor, the PTO also stops.
Commonly used in mini tractors (below 35 HP) that do not require constant PTO use.Dual Clutch: It has two clutch plates controlled by a single pedal with two stages.
Half-press stops the wheels (for gear shifting).
Full-press stops both the wheels and the PTO.
Dual clutch systems are ideal for medium-range tractors used for both driving and PTO applications.Double Clutch: Similar to dual clutch but with two separate control systems, one foot pedal for the wheels and one hand lever for the PTO.
This setup allows the tractor to stop without halting the implement, ensuring smoother operation during fieldwork.
B. Based on Lubrication:
Dry Clutch: Works without oil. It’s simple, cheaper to maintain, and ideal for light-duty tractors. However, it can wear out faster since there’s no oil for cooling or lubrication.
Wet Clutch: Operates in an oil bath, keeping the clutch cool and reducing wear.
It’s quieter, lasts longer, and is suitable for heavy-duty tractors that run for long hours. The only downside is that it’s costlier and more complex to repair.

2. Gearbox: The Speed and Power Controller
The gearbox determines how power from the engine is transmitted to the tractor’s wheels. It allows the tractor to operate at different speeds and torque levels depending on the type of farming task.
For example:
Low gears = high torque, low speed (ideal for ploughing or pulling heavy loads).
High gears = low torque, high speed (useful for transport or light work).
Types of Gearboxes (Based on Internal Design):
Sliding Mesh Gearbox: In this system, gears are physically slid into position. It’s simple and affordable, but it can be rough during gear shifting. Mostly found in older tractor models.
Constant Mesh Gearbox: Here, all gears remain constantly engaged, and dog clutches are used to select gears. It allows smoother shifting and lasts longer than sliding mesh systems.
Synchromesh Gearbox: A more advanced version where synchronizers make gear shifting smoother and easier. It is used in modern tractors for better performance and comfort.
Types of Gear Systems (Based on Function):
Manual Transmission: The driver manually selects gears. It provides full control, making it ideal for Indian farmers who prefer flexibility and cost efficiency.
Power Shift or Automatic Transmission: Gear changes happen automatically without using the clutch. It’s convenient but expensive, used mostly in high-end tractors.
Hydrostatic Transmission: Uses hydraulic fluid instead of gears to transfer power. It offers seamless speed control but is costlier and requires more maintenance.
Continuous Variable Transmission (CVT): Offers infinite gear ratios, meaning smooth acceleration and perfect speed adjustment. Found in premium tractors for maximum efficiency.
Also Read: Hidden Cost of Buying a Tractor in India Every Buyer Must Know About
3. Differential: The Turning Assistant
The differential is a set of gears that allows the rear wheels of the tractor to rotate at different speeds, especially while turning.
When a tractor takes a turn:
The outer wheel covers more distance and needs to move faster.
The inner wheel covers less distance and needs to move more slowly.
Without a differential, both wheels would rotate at the same speed, causing slippage, soil damage, and extra tyre wear.
In short, the differential ensures smooth, balanced turns while maintaining stability and traction.
4. Final Drive: The Torque Booster
The final drive is the last stage of the power transmission system. It reduces the rotational speed coming from the differential and increases torque before sending power to the axles.
This mechanism helps tractors perform heavy-duty operations such as:
Ploughing tough soil.
Pulling trailers or trolleys.
Operating heavy implements like rotavators or cultivators.
The final drive ensures that tractors maintain high pulling power even at low speeds. Without it, tractors would struggle on uneven or heavy terrain.
5. Axles: The Power Deliverers
The axles are solid metal shafts that deliver power from the final drive to the tractor’s wheels. They also help in maintaining stability, balance, and shock absorption on uneven fields.
Axles bear the tractor’s load and ensure the wheels rotate correctly as per the power received from the engine.
Types of Tractor Axles:
Front Axle: Located at the front, it helps steer the tractor. In 4WD (four-wheel drive) tractors, it also helps transmit power to the front wheels for better grip and traction.
Rear Axle: The main driving axle in most tractors. It carries the tractor’s weight, transfers power from the gearbox, and supports the differential and final drive.
Stub Axle: A smaller axle connected to the front wheels that helps in turning and steering. It absorbs shocks when operating on rough or uneven land.
Also Read: How to Save Your Tractor Clutch from Early Damage: Easy Tips for Long Life and Smooth Farming
How Do All These Parts Work Together?
Here’s how power flows through the system:
An engine produces power through combustion.
The clutch connects or disconnects this power to the transmission system.
Gearbox adjusts speed and torque according to the task.
Differential distributes this power to both rear wheels while allowing speed differences during turning.
Final Drive reduces speed and increases torque for efficient operation.
Axles transfer this power to the wheels, allowing movement.
Every single part is essential. If one fails, the tractor’s performance can drop drastically. That’s why regular maintenance and oil checks are crucial for the transmission system’s long life.
Maintenance Tips for Tractor Transmission System
Proper care of the transmission system ensures your tractor runs smoothly and efficiently for years.
Here are a few tips:
Regularly check and replace transmission oil as recommended by the manufacturer.
Avoid changing gears roughly to prevent clutch wear.
Clean air filters and cooling systems to prevent overheating.
Check for any oil leaks or abnormal noises in the gearbox or differential.
Schedule regular servicing and inspection by authorised mechanics.
Why Understanding Transmission Matters for Farmers

For a farmer, a tractor is more than a machine; it’s a partner in productivity. Choosing the right transmission system helps in:
Saving fuel: Efficient power transfer reduces fuel consumption.
Increasing productivity: Smooth gear shifts and torque control make tasks faster.
Reducing maintenance costs: Proper clutch and gear selection extends tractor life.
Improving comfort: Modern transmissions like CVT or hydrostatic offer smoother rides with less fatigue.
Whether you are a small-scale farmer or running commercial agriculture, understanding how transmission works helps you make smarter buying decisions.
Also Read: How to Service a Tractor at Home: Top 5 Easy Tips for Farmers
Key Differences Between Transmission Types
Transmission Type | Control | Advantages | Common Use |
Manual | Driver-operated | Affordable, full control | Most Indian tractors |
Automatic (Power Shift) | Automatic | Easy to operate, smooth shifts | High-end tractors |
Hydrostatic | Hydraulic control | Infinite speed control | Advanced models |
CVT | Continuously variable | Seamless power delivery | Premium tractors |
Importance of Choosing the Right Transmission System
Every type of farming requires a different performance from the tractor.
For heavy-duty fieldwork (like ploughing, rotavating, or hauling): choose a manual or dual clutch transmission for maximum torque and control.
For commercial or transport work, synchromesh or automatic transmissions offer smoother rides.
For advanced operations, CVT and hydrostatic transmissions provide better speed control and operator comfort.
Choosing the wrong transmission can lead to poor fuel efficiency, reduced performance, or faster wear of internal parts.
Future of Tractor Transmissions
Modern tractor manufacturers are focusing on technology-driven transmissions. With the rise of electric tractors and precision agriculture, transmission systems are evolving to offer automatic control, better torque management, and reduced energy loss.
Some companies are also developing intelligent power transmission systems that adjust automatically based on field conditions, saving time and energy.
As agriculture becomes more mechanised, transmission technology will continue to improve, providing farmers with smoother, more powerful, and efficient tractors.
Also Read: International Day of Awareness of Food Loss and Waste 2025: Promoting Sustainable Food
CMV360 Says
The tractor transmission system plays a key role in ensuring that every bit of power generated by the engine is effectively used for farm operations. From the clutch to the gearbox, differential, final drive, and axles, every part works in harmony to provide speed, torque, and control.
By understanding how transmission works and maintaining it properly, farmers can ensure long life, efficiency, and productivity from their tractors.
FAQs
1. What is the main function of a tractor transmission system?
It transfers power from the engine to the wheels, controlling the tractor’s speed, direction, and torque.
2. What are the main parts of the tractor transmission system?
The five main parts are the clutch, gearbox, differential, final drive, and axles.
3. Do tractors have manual transmissions?
Yes, most Indian tractors use manual transmission for better control and cost efficiency.
4. Are dual clutch and double clutch the same?
No, a dual clutch uses a single pedal with two plates, while a double clutch uses two separate controls (pedal and lever).
5. What are the types of axles in a tractor?
Front axle, rear axle, and stub axle.
6. Can regular maintenance extend the life of the transmission system?
Yes, timely oil changes, cleaning, and inspections help prevent damage and improve performance.
Features & Articles
Single and Double Clutch in Tractors: Which One Is the Right Choice for Your Farming Needs?
Compare single vs double clutch tractors. Learn differences, benefits, and which clutch suits your farming needs for better efficiency, comfort, and long-term value....
02-Feb-26 12:22 PM
Read Full NewsTop 10 Tractor Brands in India 2026
Explore the top 10 tractor brands in India for 2026 with prices, features, and uses. A simple guide to help farmers choose the right tractor....
23-Jan-26 11:48 AM
Read Full NewsTop 5 Mahindra Tractors Under ₹5 Lakh for Small Farmers in India (2026)
Explore the best Mahindra tractors under ₹5 lakh with prices, features, and comparisons. A simple 2026 guide for small farmers seeking affordable, reliable, and fuel-effi...
22-Jan-26 01:03 PM
Read Full NewsMukhya Mantri Ladli Behna Yojana 2026: Complete Updated Guide to Benefits, Eligibility, Application Process, and Impact
Complete guide to Mukhya Mantri Ladli Behna Yojana 2026 covering benefits, ₹1,500 monthly assistance, eligibility rules, application process, DBT payments, latest updates...
21-Jan-26 12:24 PM
Read Full NewsSub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM): Complete Guide
Complete guide to Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization covering objectives, subsidy structure, eligibility, benefits, funding pattern, and online application process...
16-Jan-26 06:26 AM
Read Full NewsTop 10 Types of Farming Practiced in India 2026: Explained with Crops, Benefits and Schemes
Explore the top 10 types of farming in India with meaning, benefits, crops grown, modern methods, key factors, and government schemes supporting sustainable and profitabl...
15-Jan-26 09:43 AM
Read Full NewsAd
Ad
As featured on:


Registered Office Address
Delente Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
M3M Cosmopolitan, 12th Cosmopolitan,
Golf Course Ext Rd, Sector 66, Gurugram, Haryana
pincode - 122002